Toppling of water heater's hot water tanks; poor installation hidden till the big earthquake (referring to Kumamoto earthquake related inquiries)
In connection with the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake occurred on Thursday, April 14, 2016 and afterwards (hereinafter called "the Kumamoto earthquake"), consumer centers in the devastated area and the National Consumer Affairs Center of Japan (hereinafter called "NCAC") received inquiries and complaints about damage caused by toppled or tilted hot water tanks of water heater facilities such as electric or gas water heaters and natural refrigerant CO2 heat pump water heaters (hereinafter called "water heaters").
Troubles associated with toppling of water heater's hot water tanks were also reported after the Great East Japan Earthquake. NCAC issued an alert to consumers and made a request to businesses concerned at that time. Based on the previous instance, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism partly revised a "Public Notice specifying the safe load bearing structure method for building equipment" to clarify criteria for taking measures to prevent building equipment from toppling. Nevertheless, numerous hot water tanks toppled in the Kumamoto Earthquake, probably due to poor installation.
A water heater's hot water tank is big and heavy. Toppling of a hot water tank may cause a serious accident. Therefore, NCAC decided to share key points to prevent hot water tanks from toppling as well as consultation cases related to hot water tanks toppled in the Kumamoto Earthquake.
Outline of inquiries registered in PIO-NET (Practical Living Information Online-Network System) 1
(1) Number of inquiries
From the occurrence of the Kumamoto Earthquake on April 14 through October 3, PIO-NET received 3,152 inquiries related to the Kumamoto Earthquake. Of these, 82 cases are about toppled hot water tanks of water heaters.
(2) Prefectures where inquirers live
Of these 82 cases reported after the Kumamoto Earthquake, 79 cases were from Kumamoto, 2 cases were from Oita, and 1 case was from Fukuoka.
(3) Comparison with the number of inquiries related to the Great East Japan Earthquake
NCAC compared the number of inquiries received in about 6 month period 2 from the occurrence of the Great East Japan Earthquake and that from the occurrence of the Kumamoto Earthquake, as well as the number of inquiries about toppled hot water tanks among the aforementioned two. Considering that the area devastated by the Great East Japan Earthquake was larger and was also damaged by Tsunami as well as the nuclear accident, it is not appropriate to make a simple comparison between inquiries related to the Great East Japan Earthquake and those related to the Kumamoto Earthquake. Nevertheless, there is only a slight difference between the number of inquiries about hot water tanks toppled in the Great East Japan Earthquake and that in the Kumamoto Earthquake.
- 1 PIO-NET (Practical Living Information Online-Network System) is a database that collects information on inquirie s concerning consumer affairs by linking the National Consumer Affairs Center of Japan (NCAC) with local consumer centers and similar organizations across Japan via an online network.
- 2 With regard to the Kumamoto Earthquake, data received from April 14, 2016 through October 10, 2016 (5 months and 20 days) were used.
| Earthquake name | Number of inquiries received in six month period from the occurrence of the earthquake | Number of inquiries about toppled hot water tanks |
|---|---|---|
| Great East Japan Earthquake | 25,515 | 104 |
| Kumamoto Earthquake | 3,152 | 82 |
(4) Age of toppled hot water tanks
Among the cases of toppled hot water tanks, the year of installation was identified in 55 cases. The average age of the 55 hot water tanks was 7.1 years. The minimum age was 2 months, while the maximum age was 28 years. About half of the tanks were installed within the past 5 years, which means they were installed after the Great East Japan Earthquake.
Diagram 1: Number of years from installation
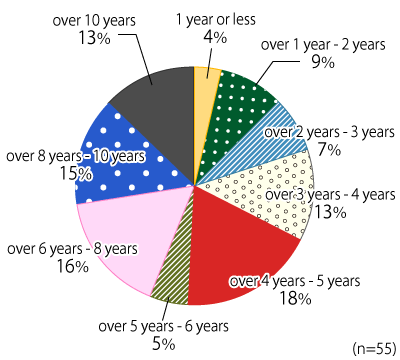
Toppled hot water tanks aged 1 year or less account for 4%. Those aged over 1 year to 2 years account for 9%. Those aged over 2 years to 3 years account for 7%. Those aged over 3 years to 4 years account for 13%. Those aged over 4 years to 5 years account for 18%. Those aged over 5 years to 6 years account for 5%. Those aged over 6 years to 8 years account for 16%. Those aged over 8 years to 10 years account for 15%. Those aged over 10 years account for 13%.
How to install a hot water tank
Diagram 2: Visualization of how to install a hot water tank with anchor bolts
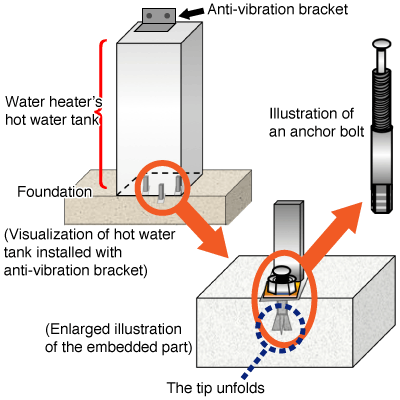
A water heater's hot water tank is stabilized with anchor bolts which are specified depending on the installation site, the position to be anchored, and the maximum water volume of the tank.
Anchor bolt:
In order to stabilize legs of the hot water tank, anchor bolts are embedded in the foundation. Each anchor bolt is inserted in a hole drilled in the foundation. When the core rod head is hammered down, sleeves below unfold and dig into the foundation. Then, each leg of the tank is hooked on the bolt head and tightened with a nut to provide stability. Anchor bolts are divided into several categories according to screw diameter, such as M10 (about 10 mm) and M12 (about 12 mm). Each of these categories has variety of lengths. Depending on the installation site, the upper part of the hot water tank may be bolted to wall.
Anti-vibration bracket:
It is used for bolting the upper part of the hot water tank to wall or other structure.
Major consultation cases
About 80% of the inquiries of toppled hot water tanks are associated with poor installation. Specifically, inquirers complained that anchor bolts did not meet requirements written on installation instructions in terms of size, the number of bolts, and the way of securing to the foundation.
- [Case1] The installation instructions specify to use M12 anchor bolts, but actually M8 anchor bolts were used.
- A water heater's hot water tank which was installed 10 years ago toppled down in the earthquake. The manufacturer's installation instructions stated as follows: "M12 anchor bolts shall be used to secure the hot water tank to the foundation. A fall prevention bracket shall be installed at the upper part of the hot water tank". Actually, however, M8 anchor bolts (diameter: 8 mm) were used and a fall prevention bracket was not installed on it. I pointed out to the installer that the hot water tank would not have toppled in the principal earthquake if it had been installed as written on the installation instructions. The installer told that M8 anchor bolts had been commonly used 10 years ago. I am dissatisfied with the response.
- (received in May 2016, contract signatory: man in his 30s in Kumamoto, unemployed)
- [Case2] A water heater's hot water tank was just placed on two concrete blocks and was not bolted.
- A water heater's hot water tank which had been installed 19 years ago toppled and bumped into a fence in the earthquake. Water leaked from the hot water tank. No other hot water tank toppled in my neighborhood. I checked the status of the toppled hot water tank and noticed that it had been just placed on two concrete blocks and the upper part was not bolted. Soon after the earthquake, I asked the dealer to check on it. The person in charge who visited me just touted new products. A contact person of the manufacturer told me that the hot water tank had been poorly installed.
- (received in May 2016, contract signatory: woman in her 40s in Kumamoto, unemployed)
- [Case3] When checking the foundation of a toppled hot water tank, I noticed that the tank had been just placed on the foundation without being bolted at the bottom.
- A water heater's hot water tank which had been installed about two and half years ago toppled in the earthquake, and since then it has been leaning against next door's wall. Seeing the foundation, I noticed that the hot water tank had been just placed on it. If the tank is left as it is, it may topple down. I requested the contractor to redo installation right away, but there is no reply. I asked the manufacturer to inspect the status. After the inspection, the manufacturer pointed out that the tank had not been bolted, which means manufacturer's standard specification had not been followed.
- (received in May 2016, signatory contractor: woman in her 50s in Kumamoto, self-employed)
- [Case4] It was bolted at a position different from that specified by the installation instructions.
- When I built a new house 6 years ago, a water heater's hot water tank with three legs was installed on a concrete foundation attached to the foundation of my house. The hot water tank toppled in the earthquake. One of the anchor bolts was inserted between the two foundations. The installation instructions specify that anchor bolts shall be bolted 60 mm or more inside from the edge of the foundation. I consulted a research institution, who told that it had been wrongly installed. Then I inquired the home builder and the subcontractor about it. The subcontractor didn't know the existence of installation instructions. The home builder insisted that the installation had not been defective.
- (received in May 2016, contract signatory: man in his 30s in Kumamoto, salary earner)
- [Case5] Since the concrete foundation was so thin, anchor bolts came out of the foundation and the hot water tank toppled down.
- I bought a new house with a water heater's hot water tank, which was handed over two months before the earthquake. The hot water tank toppled when anchor bolts came out of the foundation in the earthquake. The toppled tank damaged a fence around my house. When the contractor replaced the old hot water tank with a new one, it was found out that bolts initially used were different from those specified by the manufacturer. So I requested the contractor to use the specified longer bolts. The concrete foundation of the hot water tank was so thin and the bolts penetrated through the foundation. Therefore, the foundation had to be rebuilt. Later, I received a bill for construction including the foundation construction. I don't understand why I have to pay for the water heater in full, since the initial construction was defective.
- (received in May 2016, contract signatory: man in his 30s in Kumamoto, salary earner)
- [Case6] The foundation which stabilized a hot water tank was not secured to the ground.
- A water heater's hot water tank which was installed 8 years ago toppled from the base in the earthquake. The hot water tank was secured to the base, but the base was not secured to the ground. I thought that the base had a concrete foundation below till the tank toppled down. Actually, there were a few concrete blocks, between which polystyrene like object was placed. It appeared that the surface was just coated with concrete. The water heater became useless, but still the payment remains outstanding. The damage occurred because of poor installation, so it goes against the grain to pay all the cost for the water heater.
- (received in May 2016, contract signatory: man in his 70s in Kumamoto, unemployed)
- [Case7] A toppled hot water tank damaged the next house.
- A water heater's hot water tank was installed when my house was newly built 10 years ago. The hot water tank toppled in the principal earthquake. The toppled hot water tank damaged next door's wall, dented the back of a car and broke its glass. Installation instructions specify that M12 anchor bolts shall be used to support the 460 kg electric water heater. When I inquired the installer, they told that they had not followed the installation instructions. I requested the installer to repair the equipment right away, but they replied "We cannot repair it. It has to be replaced with a new one, which will cost about 400,000 yen". I'm dissatisfied with the response.
- (received in May 2016, contract signatory: woman in her 40s in Kumamoto, salary earner)
Difficulties
(1) Installation instructions were not followed.
Each manufacturer of water heaters attaches installation instructions to its products in order to ensure firm and safe installation of hot water tanks. Nevertheless, there have been many cases where a hot water tank toppled in the Kumamoto Earthquake probably because installation instructions had not been followed. Problems of poor installation were mostly found in the following respects.
- Foundation related problems: There was no foundation. / The foundation was thin. / The foundation was not secured to the ground. [Case 2, 5, 6]
- Number & position of embedded anchor bolts: There was no anchor bolt. / Only one anchor bolt was embedded. / An anchor bolt was embedded in a wrong position. [Case 2, 3, 4]
- Size of anchor bolts: M10 or M8 anchor bolts were used although the installation instructions stated to use M12 anchor bolts. / Anchor bolts shorter than those specified were used. [Case 1, 5, 7]
(2) Poor installation is likely to be overlooked.
A hot water tank can stand by itself, and its legs are covered over. Therefore, poor installation is hardly found by appearance before the tank topples due to a big earthquake or other force.
(3) Sometimes it is unclear who is responsible for installation.
It is common that several companies are involved in installation of a water heater, such as a foundation constructor, an equipment installer, a home builder and a water heater manufacturer. If so, it may not be easy for consumers to identify who is responsible for poor installation. Even if a consumer inquires a contractor about poor installation, the contractor might not respond to it.
(4) Lessons learnt from the Great East Japan Earthquake were not utilized.
In light of the numerous hot water tanks toppled in the Great East Japan Earthquake, NCAC, relevant ministries and industry associations took preventive measures, such as issuing an alert to consumers, revising a public notice, raising awareness among businesses, etc. As a result of these actions, sellers and installers of water heaters probably had opportunities to get information on hot water tanks toppled in the earthquake, at least after September 2011.
Among inquiries about toppled hot water tanks received after the Kumamoto Earthquake, NCAC analyzed cases where the number of years from installation was identified (see the aforementioned 1.(4) Age of toppled hot water tanks). Hot water tanks installed after the enforcement of the revised public notice (after April 2013) account for 20%. Hot water tanks installed after the Great East Japan Earthquake including those installed after April 2013 account for about 50%.
According to the data, it appears that the proper installation method without safety problems is yet to be spread and conducted across Japan and that lessons learnt from the Great East Japan Earthquake were scarcely utilized.
Advice for consumers
(1) If a water heater has been already installed
- Check if the water heater has been installed as specified by the installation instructions. If you don't have the installation instructions, inquire the manufacturer about it. If you don't know where to be checked, or if it is difficult to check by yourself, ask the installer for help.
- If the installation instructions were not followed, inform the installer about it and request the installer to secure the hot water tank.
- Even if the initial construction satisfied the requirements of the installation instructions, anchor bolts may be loosened after many years. If you have any concerns, request the installer to check the equipment. In that case, remember to ask if the inspection is free of charge or not.
(2) If a water heater will be installed
- When installing a water heater, make sure if the installation instructions are followed, together with the installer.
- Keep documents from the installer throughout the period of use of the water heater.
- If you have any question about installation, ask the manufacturer or installer about it till you understand.
(3) Ask any unclear questions
Even if you haven't encountered trouble, consult your local consumer center if you have any unclear questions. 3
- 3 Consumer hotline: 188
It is a three digit phone number which connects you to your local consumer center.
Request to industry associations
NCAC already issued a request to industry associations on July 21, 2011. In light of the ensuing revision of the public notice and consultation cases related to the Kumamoto Earthquake, NCAC further requests them to take the following actions.
(1) To water heater manufacturers
- To make and use installation instructions which meet "criteria for taking measures to prevent water heater equipment from toppling" written on the revised public notice.
- To draw up a construction checklist which allows consumers to easily understand and check details of construction as closely as possible.
- To encourage sellers and installers to inspect water heater equipment already installed and to take measures to ensure proper construction as specified by the installation instructions.
(2) To sellers and installers
- To inspect equipment already installed. It may have become unstable due to poor installation or an earthquake.
- To ensure proper construction as specified by the installation instructions.
- To inform consumers whether or not their construction followed the installation instructions, and to hand over relevant documents including the installation instructions to consumers.
Reference
Example of a hot water tank toppled in the Kumamoto Earthquake

